Why Is Personal SEO Essential For Your Career Success?
1,179,448,021. Go back and read that again.
Just like you ignored the numbers the first time around, search engines too will ignore your results when they index their search results — unless you’ve optimized your personal SEO.
In case you were wondering, that number is the current amount of websites on the internet — of which roughly 20% are actively up and running at any given time.
That’s a massive number of listings that you’ll have to compete with in order to rank well on SERP— short for Search Engine Results Pages.
Throughout the course of this article, you’ll learn the importance of personal SEO and how it affects your personal brand (which in turn affects your career prospects), as well as tips to improve said SEO.
Terminology
It’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with the following terms and connotations, especially if this is your first time hearing the word “SEO”.
- SEO
Stands for Search Engine Optimization refers to the delicate art of making a website appear on the results page of a search engine when a particular keyword is searched for.
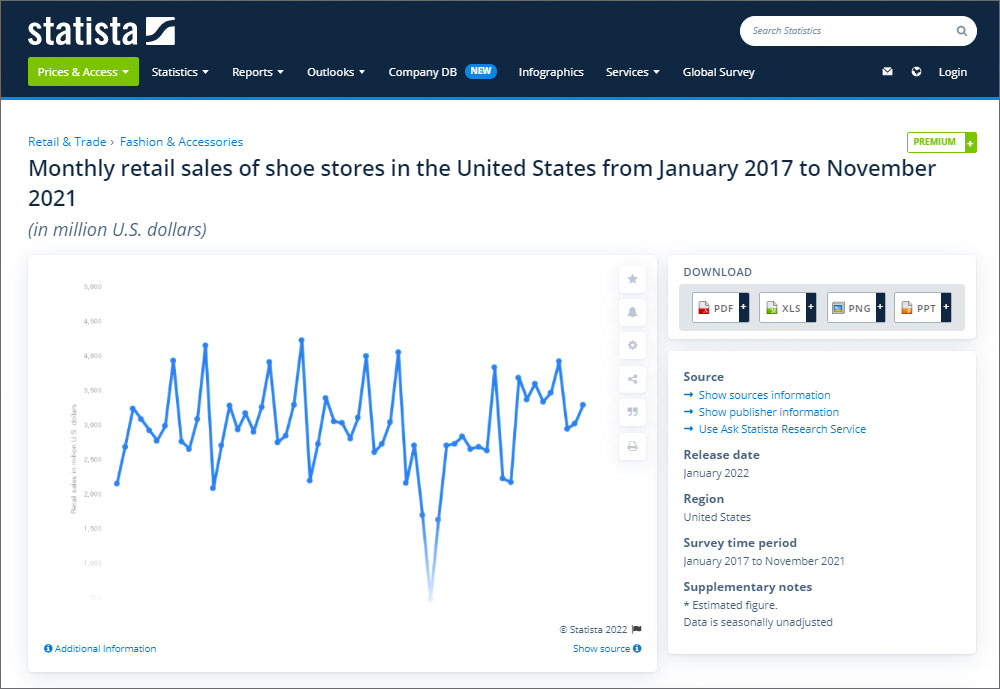
E.g. If someone types in “sneakers men”, the top results are Nike, Adidas, and Nordstrom (all shoe sales sites).
- SERP
Stands for “Search Engine Results Page”, and is usually used to refer to the first ten results associated with a keyword.
Given that only 6% of users even go to the second page of search results, it’s a game-changer to rank in the first ten results (so you appear on page one).
Even so, the bottom five results only receive ~4% of total clicks, so the spot you really want to aim for is the top five.
You’ll be shocked to learn that the top five results for a particular keyword, on average gobble up about 68% of all traffic (click-through rates).
- Crawling
This is the technical name for the process that all search engines follow when indexing search results.
It is the deciding factor that determines your ranking on the SERPs.
Put simply, crawling refers to the process of any given search engine “following your links”.
Why?
Because the quality of your backlinks is a major factor when it comes to ranking well on search engines.
- Personal SEO
This refers to the continuous process of improving the SEO for your personal website so that you (as a brand and as a website) rank well in relation to set keywords.
For example, if you are a photographer or freelance coder, you want your website(s) to appear when keywords/ strings like “programmer” and “photographer near me” are searched for.
How Personal SEO Benefits Your Career
Optimizing your personal is actually much more beneficial than you realize. Here are a few (non-exhaustive) points:
- When a potential employer searches for your name, you want your personal website to be top of the list, not your Facebook profile with embarrassing pictures from 2015.
- The same applies for potential clients/ customers.
- You can be shortlisted for interviews based on your personal website.
In today’s neo-modern, pro-tech world, your website often outweighs any cover letter or resume that you may have sent in.
- Since personal SEO expands to cover more than just search engines, it can also influence search results on social media networking search results like:
- LinkedIn,
- Job-seeking websites like Indeed and Glassdoor
- Even Instagram and Facebook, if that’s where you do your business
- Any other searchable websites where you have a profile.
- When done well, keywords specific to you (such as your name or current role) will have you filling up multiple results on SERPs.
This, in turn, will boost your click-through rates, which drives sales and visibility, which circles back to increasing your click-through rates.
Since not many people currently understand or comprehend why SEO is important for your online success, you have the benefit of a significant head start on your competition.
In a nutshell: personal SEO increases your visibility and helps you be seen by more people.
To be considered for a job, you need to first be found.
Having optimized personal SEO will help you be found by anyone with a simple google search for your name — think of it as an investment.
Statistics That Back What We’re Saying
We’re not just talking through our hats here. Here, let the numbers speak for themselves.
- Microsoft Study, the early 2010s
According to this Microsoft-funded study, almost 80% of employers googled their prospective candidates and active job applicants before even remotely considering them for the position they had applied for.
Although it is fairly old, it still holds valuable information on what a person’s online reputation is, and how that affects their job consideration and social visibility.
We’d definitely recommend reading through the 20-page document, as it is guaranteed to change your perspective on your online reputation.
It also points out the fact that recruiters can now anonymously collect information that they couldn’t get in an interview earlier, such as the candidate’s affiliation to various groups, their medical situation, etc.
8 out of 10 hiring managers google their candidates and assess their online presence before even considering them for a position.
- JobVite Survey, 2018
This survey has the following takeaways;
- 77% of recruiters check out their candidates on LinkedIn.
- 63% of recruiters check out their candidates on Facebook.
- 25% of recruiters check out their candidates on Instagram.
They actively look for things like:
- Engagement in local groups (good)
- Examples of the candidate’s work (good)
- Mutual connections with the candidate (good)
- Political rants by the candidate (bad)
- References to marijuana (bad)
- Pictures of alcohol consumption (bad)
- Spelling mistakes in the candidate’s posts (bad)
Here’s a quote from the report: “Social sleuthing is standard in recruiting” — which is just another reason to not ignore your SEO.
- CareerBuilder Study, 2018 (Valuable Resource Bank)
This study came to the following conclusions:
- 66% of employers admit to using search engines to research potential candidates.
- 70% of employers will check out a candidate’s Facebook before hiring them.
- 57% of employers will reject a candidate based on what they find on social media.
The article is a summary of the results of the actual study, thus it’ll barely take five minutes for you to skim through its bullet points — trust us, it’s worth it.
How Search Engines Rank Content (Including You)
All search engines have a common goal: to provide the user with the most relevant content and information for the keywords they gave as input.
Every time a user searches for something, a search engine’s algorithms swing into action to cherry-pick the pages best suited to that user’s search.
The algorithms do this in a two-step process: relevancy analysis and authority measurement.
- They Analyze Relevancy
Translation: Search engines look for connections between the content on a webpage and the input keywords defined in the search bar by the user.
The more matching, high-quality, well-positioned keywords on a page, the more marks that page scores in the eyes of that search engine.
BUT, algorithms have evolved to a point where they can easily detect “keyword stuffing”, which is basically repeated use of known keywords in an attempt to rank better.
“Shady” practices such as keyword stuffing are known as “black hat tactics” in the formal SEO world and incur severe penalties in terms of SERP rankings.
In severe cases, black hat SEO tactics can even get your website(s) completely removed from the results pages of a search engine.
(Users will still be able to access your website, but they’ll have to input the exact web address of your site into the search engine to do so).
It’s possible to recover from SEO penalties imposed by the engines, but it takes time, patience, expertise, and diligence.
More about SEO penalties in point #3.
- They Analyze Authority
Let’s keep it short and sweet: A search engine determines a website’s authority on the basis of that website’s popularity among the users.
The engine’s algorithms make the natural assumption that if a website is more popular than its competitor, its content is probably more valuable to the user than the competitors.
Therefore, the more popular website will enjoy a higher SERP ranking.
- Things That Get Your Website Penalized (Black Hat SEO)
Here are the three things that you should avoid if you remotely care about your SEO:
- Keyword Stuffing: We discussed this earlier, so let’s not duplicate the content, else the search engines might perceive this article as being keyword stuffed.
Reason: (Duplicate content is considered a big negative in the SEO world because search engines get confused as to which they should display.)
And at the heart of it, repeated keywords are just duplicated words.
- Poor Links: This includes dead links (nonexistent), broken redirects (no longer there), and irrelevant links (especially advertising).
Reason: Search engines crawl every link on your webpage before determining your ranking, and whether or not those linked pages are optimized affects your SERP ranking too.
- Long And Complicated URLs: See, a very important distinction to make is that we see websites very differently from how search engines see them.
Source: buffer.com
We see images, white space, and text; whereas a search engine only sees text. Granted, there are ways to let a search engine see images, but let’s save that for another article.
Reason: Extremely long URLs are hard for search engines to crawl, and in turn, affect the load speed of your pages, resulting in a lower ranking.
- Things That Get Your Website Brownie Points (White Hat SEO)
Now that we’ve covered the donts, let’s look at the dos.
- Put out good content: Content is the leading factor when it comes to improving your SEO — good content equals a higher SERP ranking.
Reason: Every time a user makes a search, they are looking for content about their search query — not ads.
- On-page optimization: This includes the use of optimized keywords, long-form content, H1 tags, meta descriptions, and image alt descriptions.
Reason: Remember that algorithms only look at text the first time around, so we have to make it easy for them to understand our pages.
Fact: The average #1 search result is 2416 words long.
How To Use Personal SEO To Market Yourself Online?
Well, the only question that remains is how do you, as an individual, turn the knowledge you’ve gained so far into action to better your SEO.
Let’s look at a few things you can do.
- Optimize your page (bio) on your personal website.
You definitely need to have a personal website. It’s important that people in a Google search for your name, first of all, find your website and only after that – your social networks and community profiles.
Successful SEO for a website starts with choosing the right platform. If you have HTML layout skills, feel free to choose WordPress. It’s well indexed by search engines and generally good for SEO. If you don’t have web development skills, use SEO friendly website builder software. Some of the online platforms have more SEO options than others. Just use them.
Your ‘about” page is on your own website — this means that it is your digital property and that you control most aspects of it.

It should rank above your social media profile links, including LinkedIn. Do this by;
- If your site doesn’t have a dedicated page for you, you’re on the SEO back foot. Create an “about me” page for yourself immediately if this is the case.
- Write a good bio. People should glance at your bio and know exactly what you’re about.
- Add schema tags to your bio. (This is a lengthy process, but comes in handy, so do your own research).
- If done right, part of your bio will show up as a “featured snippet” under your “About” page when people search for your name.
- Build A Strong LinkedIn Profile
After your personal website, LinkedIn is the most important search result that people look for (remember, 77% of recruiters check you out there). Improve your LinkedIn by:
- Updating your profile picture and banner.
- Customizing your LinkedIn profile URL (from the top right corner and settings).
- Don’t ignore the “endorsements” section. It’ll take some doing, but outreach messages asking for endorsements end up getting you those endorsements 95% of the time.
- Get On All Other Major Social Media Sites
Note: We’re not asking you to spend two hours a day per social networking site just to improve your SEO.
What you do need to do is use your real name and current role on those various social media sites, because social media sites tend to rank well for name searches.
Professional advice: Use the same profile picture for all your social media accounts.
If you know that you’re definitely not going to be active on that social media, just create one post that links back to your LinkedIn.
It can run something like “Hey there! You can connect with me and view my latest projects over on LinkedIn by clicking this link (insert link)”.
- Decrease Your Personal Website’s Load Time.
There are numerous ways that you can accomplish this.
Ways to improve your page’s load times:
- Image compression and optimization
- Displaying images at 100% file size
- Server-Side Rendering
- Use a CDN (content delivery network)
- Reduce the number of total HTTP requests
As a rule of thumb, in order to not get penalized by search engine indexing algorithms, your page should load within three seconds.
The Bottom Line
You might ask whether it is even possible to rank in the top three, top ten, or even top twenty results when going up against quite literally, the rest of the world.
The answer is a resounding yes — but it won’t be easy, nor will it happen overnight. Rome wasn’t built in a day.
With consistent efforts, however, it is going to be a feather in your cap, especially when you apply for a new job.
The best piece of advice we can give you is: just get started.
After all, “The journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step.” – Lao Tzu
Authored by Lesley Haught.
Lesley is an experienced writer, who has previously written for many popular websites: 2CheckOut Blog, Hackread.com, Hacked.com, 3Dcart Blog, Leadboxer.com, First5000.com.au, Contrastly.com, etc.
